
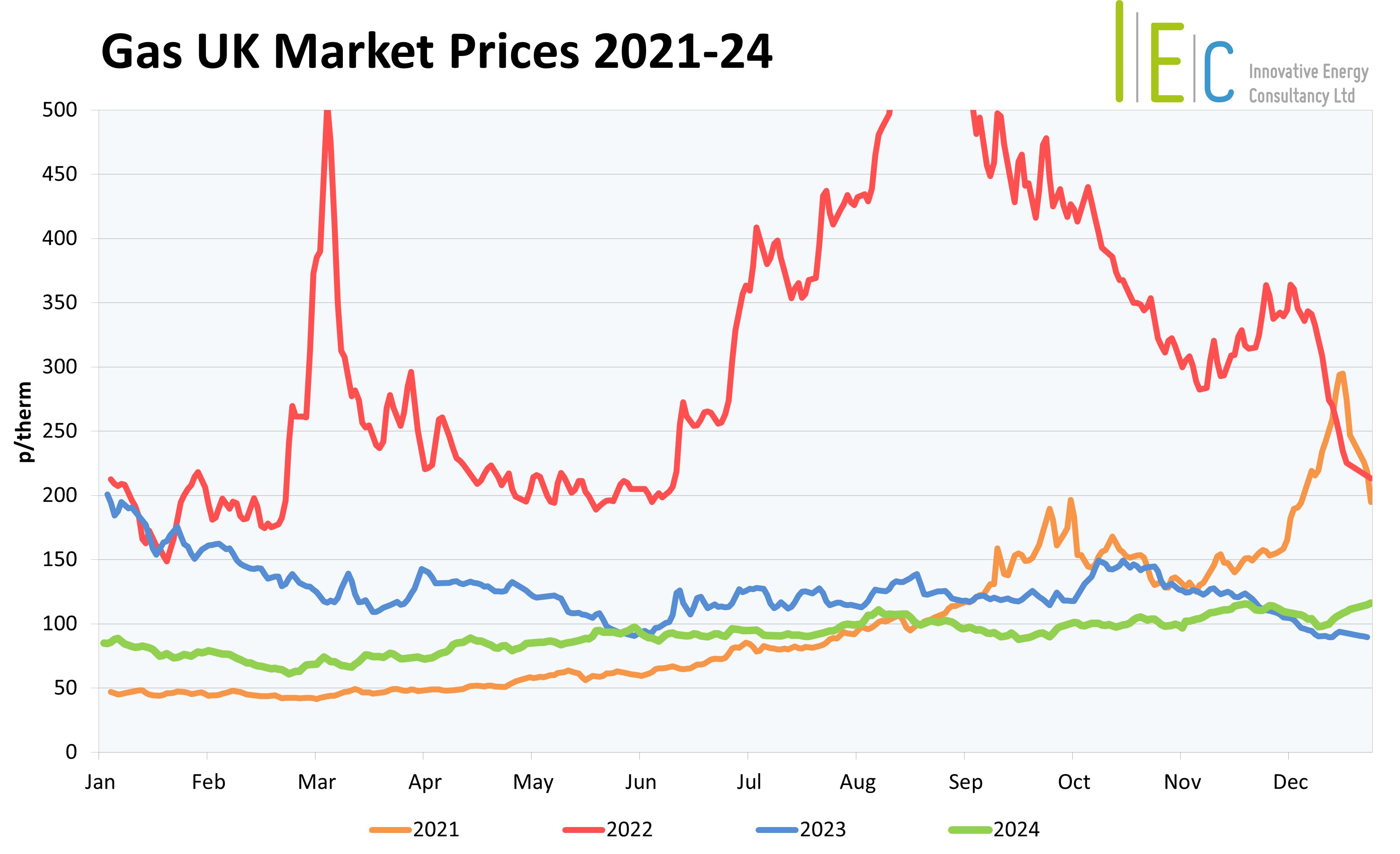
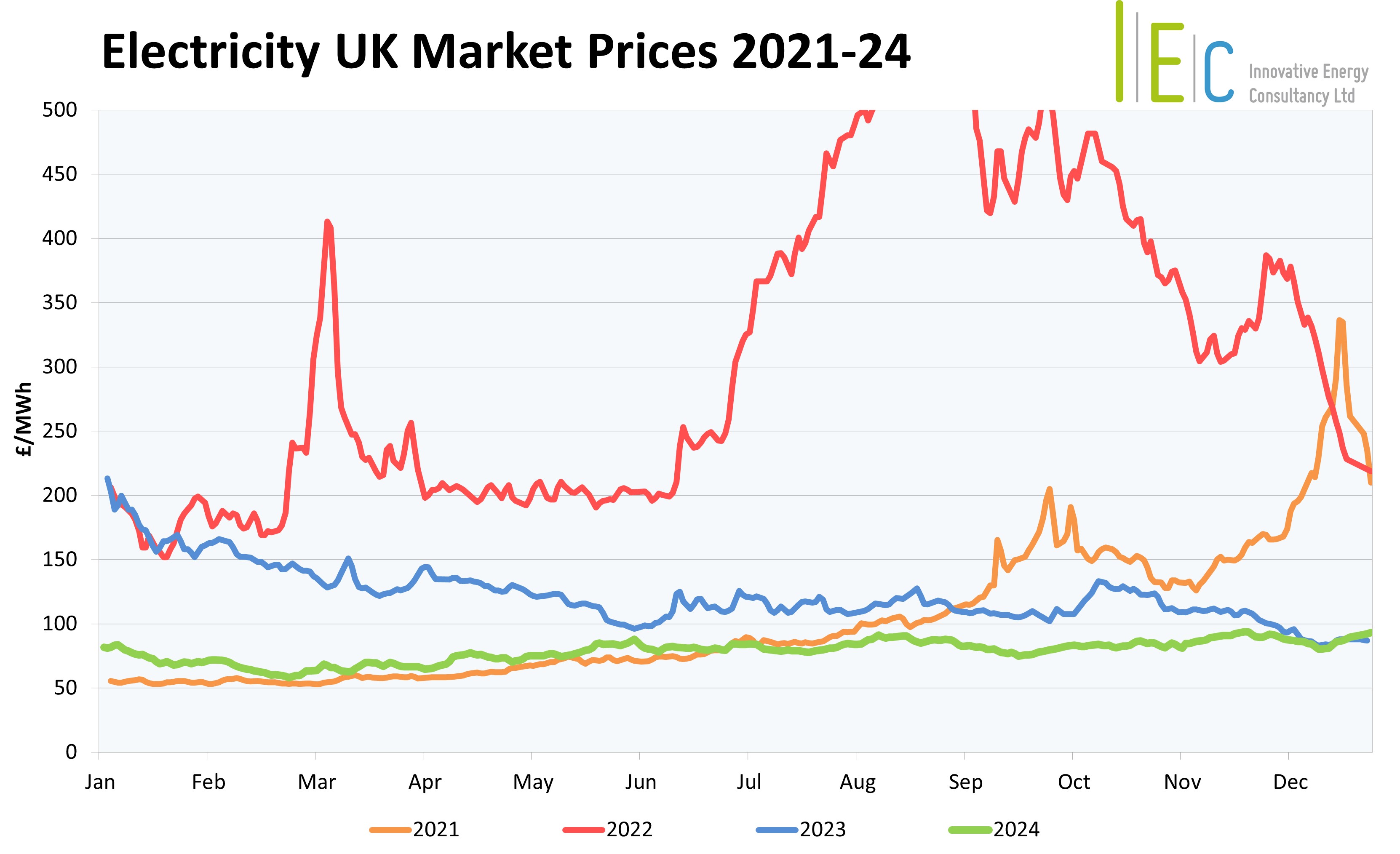
UK Gas & Electricity Market Overview – December 2024
14/01/25
The UK’s gas & electricity markets bungeed through December, experiencing a 15% drop mid-month before returning to where they started at its end. The bearish market pressures in the first half of the month were linked to the milder weather and strong LNG supplies arriving in European ports. However, these losses were then reversed, as the threat of the Russia-Ukraine gas transit deal ending became a reality on 31 December.
Ongoing Good Supply Factors
As with previous months, on average UK’s gas system was over-supplied throughout December. This was thanks to both strong pipeline flows and increasing LNG deliveries. Norwegian gas flows had minimal disruption, with only one notable unplanned outage mid-month, allowing stable supply levels to reach UK terminals, providing approximately 30% of system demand. LNG cargos continued to head to towards Europe, as China began exporting, due to weak Asian demand. EU imports reached their highest level since January 2024.
Above-Average Temperatures Return
After a cooler than average November, European temperatures returned to above average in December, bringing heating demand back in line with expected levels. Wind strengths also improved and enabled renewable generation to provide the highest percentage of the UK’s power mix, easing gas demand further. However, despite these favorable factors, both the EU and UK continued to withdraw gas from their storage facilities to meet demand, with EU levels ending the year at around 70%, well below the five-year average. With cool temperatures expected for Winter 2024/25, storage levels will remain in sharp focus until spring arrives.
Russia-Ukraine Gas Transit Deal Ends
Despite EU and US sanctions on Russian gas, around 5% of Europe’s supply continued to be pipelined through Ukraine, due to an historical agreement. However, with this due to end on 31 December, Central European countries attempted to help broker a new deal to avoid supply disruption, but to no avail. The countdown to the deadline drove December market volatility and became the most significant influence on European energy prices across the month.
Strong Renewable Power Generation
A strong month for the UK’s renewable power generation, with wind providing approximately 39% of the total mix. Additionally, milder temperatures and reduced EU demand also enabled the UK to take advantage of cheaper continental prices, importing 10% of its power from France and Belgium. Both aspects meant only 30% of the UK’s electricity was required from gas to power generation, helping to reduce some additional price volatility. The UK’s Emissions Trading Scheme (UKETS) saw its carbon price lower, ending the year at £35.38/tonne.
We meet all your
business energy needs
Find out how much money
we’ve saved for our clients,
or to arrange an informal
discussion with one of
our energy experts,
please call 01244 571830




